数学 Mathematics
数学部课程主要目标
让学生学习日常使用的数学概念和技能,并且保持学习数学的热忱
培养学生学习数学的积极态度
在学生运用数学思维解决问题时,训练他们的思维、推理、沟通、应用和元认知能力
让学生利用“思维习惯”的思维模式解决问题
数学部思维计划包括了
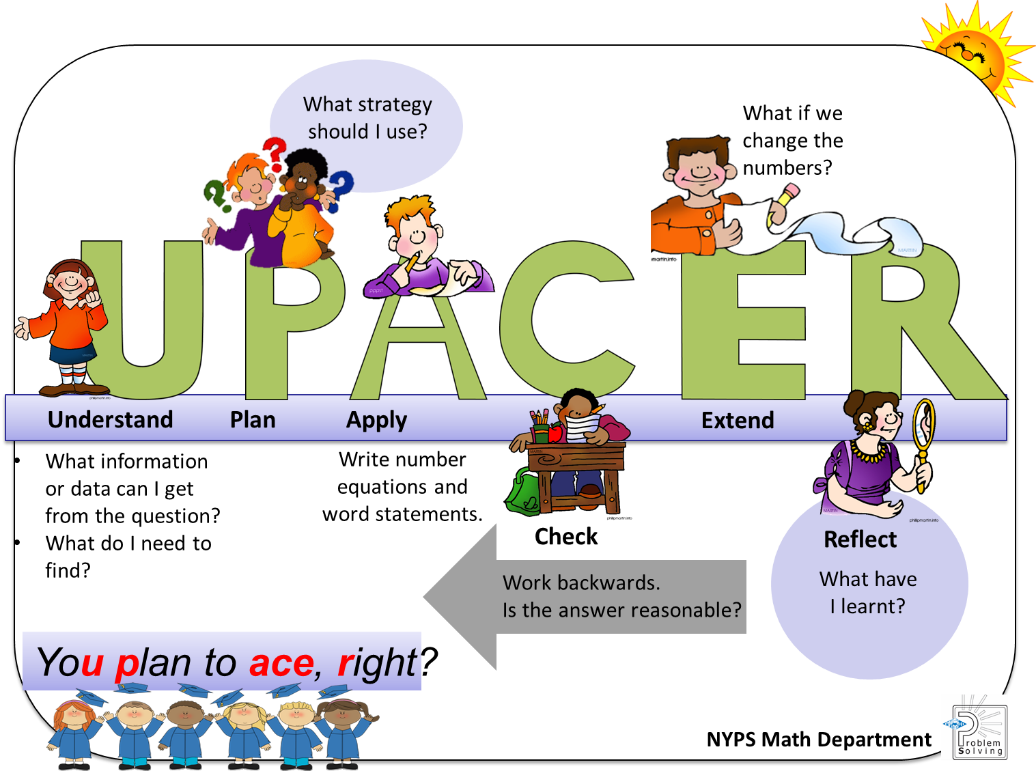
- 波利亚解题方法
- 解题是学习数学的核心。教师在教学过程中教授波利亚解题方法的四个阶段—— 理解问题、设计解题策略、按步解题、回顾解答。为了更好地满足学生的差异与学习需要,教师搭建适合学生程度的学习鹰架,提供适当的支援,以培养和扩展学生的数学推理和思维能力,并为之后的解题过程做好准备。
- 数学探索角落
“数学探索角落”的设置旨在让学生在休息期间通过各种游戏提升数学学习的乐趣。这些精心挑选出来的游戏能够推动学生数学推理和策略性思维的发展。比方说“Sleeping Queens”、“ 7 ate 9”、“Zeus on the Loose” 和 “Blokus”这几个游戏,能够促进学生策略性思维、算术技能和空间想象能力的发展。 - 思维习惯
思维习惯强调学生通过自主创造获得知识的过程。希望在智慧思维的带动下,学生可以拥有一系列高效有益的行事能力。也就是说在学生面对未知甚至困境的时候,他们将可以调动一切已有的知识与习惯,做出最有效和最适当的判断。我们的课程专注于三种思维习惯的开发——追求精确的答案、坚持以及灵活变通。这些习惯使学生能更好地运用他们的数学知识和技能来解决问题。
The key Math Programme aims to enable our students to:
- acquire Mathematical concepts and skills for everyday use and continuous learning in mathematics;
- cultivate positive Attitudes towards mathematics;
- develop Thinking, reasoning, communication, application and metacognitive skills through a mathematical approach to problem solving; and
- practise Habits of Mind when confronted with problems.
Math Thinking Programme consists of
- Polya’s Problem Solving Process
Mathematical problem solving is central to mathematics learning. The Polya’s Problem Solving steps are explicitly taught in the mathematics classroom. To better meet the diverse learning needs of our students, our teachers will vary the degree of scaffolding through differentiated instructions to develop and stretch our students’ mathematical reasoning and thinking skills for process skills worksheets.
- Math Odyssey
The Math Odyssey aims to promote joy of learning in mathematics by allowing students to explore various games during recess. The games are specifically selected to stimulate mathematical reasoning and strategy development in a collaborative setting. Some examples of the games are Sleeping Queen, 7 ate 9, Zeus on the Loose and Blokus which sharpen students’ strategic thinking along with valuable arithmetic skills and spatial visualisation skills.
- Habits of Mind
Habits of Mind is knowing how to behave intelligently when one doesn’t know the answer. The programme aims to develop 3 out of the 16 Habits of Mind, Striving for Accuracy, Persisting, and Flexible Thinking, as identified by Costa and Kallick. These habits empower the students to use their mathematical knowledge and skills to solve problems.

